 April 09, 2021
April 09, 2021
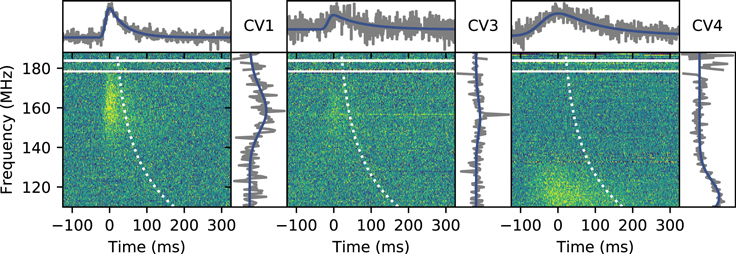
The object FRB 20180916B is a well-studied repeating fast radio burst source. Its proximity (∼150 Mpc), along with detailed studies of the bursts, has revealed many clues about its nature, including a 16.3 day periodicity in its activity. Here we report on the detection of 18 bursts using LOFAR at 110-188 MHz, by far the lowest-frequency detections of any FRB to date. Some bursts are seen down to the lowest observed frequency of 110 MHz, suggesting that their spectra extend even lower. These observations provide an order-of-magnitude stronger constraint on the optical depth due to free-free absorption in the source's local environment. The absence of circular polarization and nearly flat polarization angle curves are consistent with burst properties seen at 300-1700 MHz. Compared with higher frequencies, the larger burst widths (∼40-160 ms at 150 MHz) and lower linear polarization fractions are likely due to scattering. We find ∼2-3 rad m-2 variations in the Faraday rotation measure that may be correlated with the activity cycle of the source. We compare the LOFAR burst arrival times to those of 38 previously published and 22 newly detected bursts from the uGMRT (200-450 MHz) and CHIME/FRB (400-800 MHz). Simultaneous observations show five CHIME/FRB bursts when no emission is detected by LOFAR. We find that the burst activity is systematically delayed toward lower frequencies by about 3 days from 600 to 150 MHz. We discuss these results in the context of a model in which FRB 20180916B is an interacting binary system featuring a neutron star and high-mass stellar companion.
Pleunis, Z., Michili, D., Bassa, C. G., et al., 2021, The Astrophysical Journal Letters, Volume 911, Issue 1, id.L3, 18 pp.
