 October 19, 2023
October 19, 2023
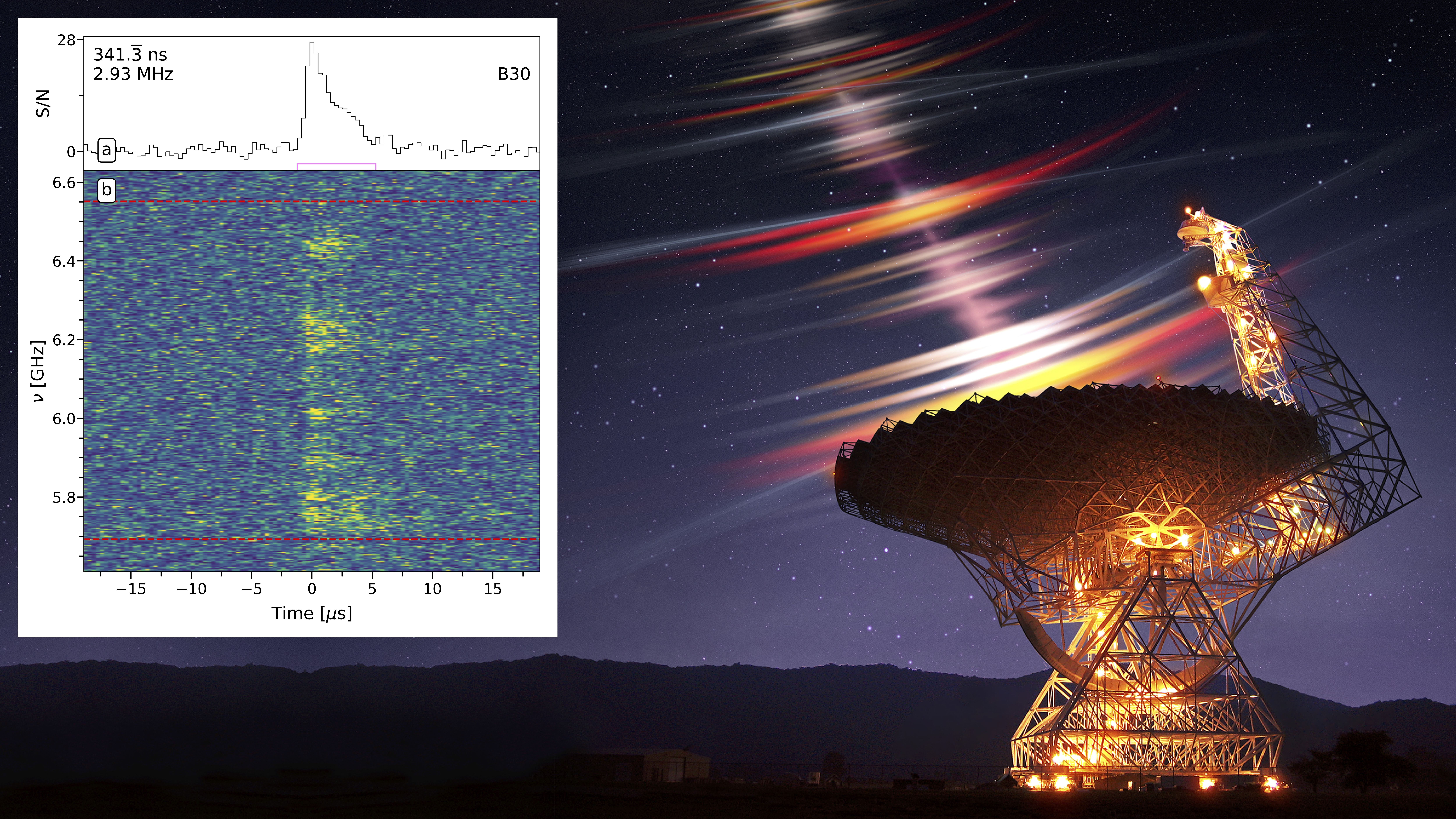
Fast radio bursts (FRBs) are extragalactic transient flashes of radio waves with typical durations of milliseconds. FRBs have been shown, however, to present a wide range of timescales: some show sub-microsecond sub-bursts while others last up to a few seconds. Probing FRBs on a range of timescales is crucial for understanding their emission physics, how to detect them effectively and how to maximize their utility as astrophysical probes. FRB 20121102A is the first known repeating FRB source. Here we show that FRB 20121102A produces isolated microsecond-duration bursts with durations less than one-tenth the duration of other currently known FRBs. The polarimetric properties of these microsecond-duration bursts resemble those of the longer-lasting bursts, suggesting a common emission mechanism producing FRBs with durations spanning three orders of magnitude. In detecting and characterizing these microsecond-duration bursts, we show that there exists a population of ultra-fast radio bursts that current wide-field FRB searches are missing due to insufficient time resolution. These results indicate that FRBs occur more frequently and with greater diversity than initially thought. This could also influence our understanding of energy, wait time and burst rate distributions.
Snelders et al. 2023, Nature Astronomy.
